In this blog, we will discuss about how deferred query
execution and Immediate Query Execution works in LINQ, and what the difference
between two are.
Deferred Execution:
Deferred execution of LINQ query means it constructs the
query/expression tree and it defers query execution until its value is requested.
When value is required, it evaluate the execution tree in locally and then it
send generated SQL to server. Deferred execution approach improves query execution performance
by avoiding unnecessary database call.
Here is an example of Deferred LINQ query:
IQueryable<Order>
orders = _dbContext.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderNumber == orderNumber);
foreach (Order item in orders)
{
new OrderData
{
OrderID = item.OrderID,
OrderNumber = item.OrderNumber,
OrderStatusCode = item.OrderStatu.StatusCode
};
}
For above LINQ query, the SQL is not generated until the foreach statement executes.
Expression
tree – expression tree is a data structure, which holds LINQ to
SQL query, which will be sent to SQL server /database.
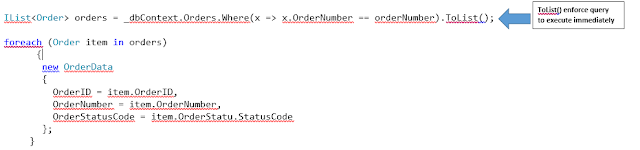
Immediate Execution:
Immediate
execution of LINQ means it enforces the LINQ query to execute and get the
result immediately and there are many methods like ToList(),ToArray(), ToDictionary()
executes the LINQ query immediately.
IList<Order> orders = _dbContext.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderNumber ==
orderNumber).ToList();
foreach (Order item in orders)
{
new OrderData
{
OrderID =
item.OrderID,
OrderNumber =
item.OrderNumber,
OrderStatusCode =
item.OrderStatu.StatusCode
};
}




No comments:
Post a Comment