XML
Serialization Process converts .net object into XML format and by default object property or class name becomes XMLElement or root element until there is
explicitly set ElementName or AttributeName property for XMLElement or
XMLAttribute.
Here is an
example without element Name or attribure Name
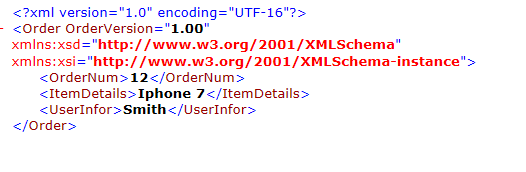
public class Order
{
public int OrderNumber { get; set; }
public string Item { get; set; }
public string User { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute]
public string version { get; set; }
}
XML String:
Now let
specify element name and attribute name for each XML Element and XML Attribute
tags
public class Order
{
[XmlElement(ElementName = "OrderNum")]
public int OrderNumber { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "ItemDetails")]
public string Item { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "UserInfor")]
public string User { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute(AttributeName="OrderVersion")]
public string version { get; set; }
}
XML String:
Add Namespace as Prefix to XML element
or attribute:
We will learn
how to add namespace as prefix to XML element or attribute
·
First,
we need to define XmlSerializerNamespaces class object, which hold reference of
namespace and its prefix.
·
Second,
we need to specify of namespace of XMLElement
ot XMLAttrbute, which we want to set
namespace as prefix for their name
public class Order
{
[XmlElement(ElementName = "OrderNum", Namespace= "http://sample.com")]
public int OrderNumber { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "ItemDetails")]
public string Item { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "UserInfor")]
public string User { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute(AttributeName = "OrderVersion")]
public string version { get; set; }
[XmlNamespaceDeclarations]
public XmlSerializerNamespaces xmlns = new XmlSerializerNamespaces();
public Order()
{
xmlns.Add("sample", "http://sample.com");
}
}
XML String:
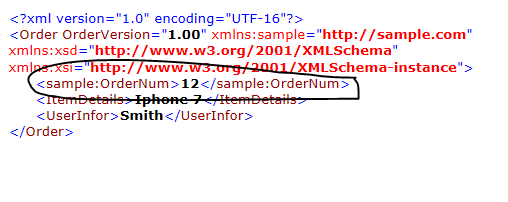
Now you can
see in above XML string, it has <sample:OrderNum>12</sample:OrderNum>
xml element tag with namespace as prefix in place of <OrderNum>12</OrderNum>
Same thing we
can apply for XMLAttribute xml tag also, we can set attribute name with
namespace as prefix
Here is an
example for XMLAttribute tag, having namespace as prefix for attribute name
public class Order
{
[XmlElement(ElementName = "OrderNum", Namespace= "http://sample.com")]
public int OrderNumber { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "ItemDetails")]
public string Item { get; set; }
[XmlElement(ElementName = "UserInfor")]
public string User { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute(AttributeName = "OrderVersion", Namespace = "http://sample.com")]
public string version { get; set; }
[XmlNamespaceDeclarations]
public XmlSerializerNamespaces xmlns = new XmlSerializerNamespaces();
public Order()
{
xmlns.Add("sample", "http://sample.com");
}
}
XML String:
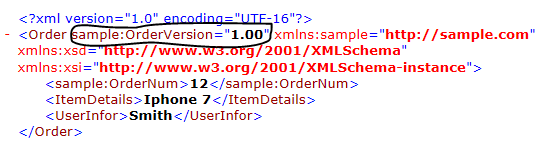
Now you can
see in above XML string, it has sample:OrderVersion
xml attribute tag with namespace
as prefix in place of OrderVersion
Other related
posts: