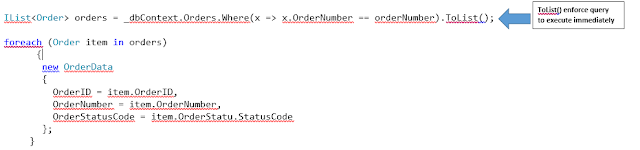
this blog will demonstrate that how Join (Left outer join, inner join) work in LINQ . LINQ has a join query operator that work like SQL JOIN. LINQ use join query operator to fetch data
from more than one tables on common columns/properties.
- INNER JOIN
- LEFT OUTER JOIN
- CROSS JOIN
There are few tables Student, StudentCourse and StudentAddress :
Student Table:
StudentID
|
StudentNumber
|
FirstName
|
LastName
|
DateofBirth
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
George
|
4/3/1989
|
3
|
913
|
Jolly
|
Singh
|
6/7/1986
|
StudentCourse Table:
StudentID
|
CourseID
|
TeacherID
|
1
|
M1
|
12
|
1
|
C1
|
13
|
1
|
E1
|
15
|
2
|
M1
|
12
|
2
|
E1
|
15
|
| | | |
StudentAddress Table:
Student ID
|
City
|
State
|
Zip Code
|
1
|
Dublin
|
OH
|
43017
|
2
|
Rockville
|
TN
|
|
Inner Join:
LINQ uses Inner Join query operator to get the data from two or more tables based on a common columns, and It will ignore those record, which are not present into both table similar Like SQL Inner Join.
 |
| INNER JOIN |
Here is an example of Inner Join in LINQ :
var query = from s in _dbContext.Students
join c in _ dbContext.StudentCourses on s.StudentID equals c.StudentID
select new { s,
c };
Lambda Expression :
var query = _dbContext.Students.Join(_dbContext.StudentCourses , s=> s.StudentID , c => c.StudentID,(s,c) => new { s, c})
.Select(m => new { m.s, m.c });
Output:
Student ID
|
Student Number
|
First Name
|
Last Name
|
Date of Birth
|
Course ID
|
Teacher ID
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
M1
|
12
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
C1
|
13
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
E1
|
15
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
George
|
4/3/1989
|
M1
|
12
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
George
|
4/3/1989
|
E1
|
15
|
In above joining query, we are fetching student and its
associated course details on given student Number (911). In this query, it
will returns only matching and common records on both tables and you can see,
there is not any record for Jolly (StudentID : 3) . StudentCourse table does
not have course details for student Jolly.
If you want to get the specific given student number records
(added where clause for Student Number)
var query = from s in _dbContext.Students
join c in _dbContext.StudentCourses on s.StudentID equals c.StudentID
where s.StudentNumber = 911
select new { s,
c };
Lambda Expression :
var query = _dbContext.Students.Join(_dbContext.StudentCourses , s=> s.StudentID , c => c.StudentID,(s,c) =>; new { s, c})
.Where(w => w.s.StudentNumber = 911)
.Select(m => new { m.s, m.c });
Output:
Student ID
|
Student Number
|
First Name
|
Last Name
|
Date of Birth
|
Course ID
|
Teacher ID
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
M1
|
12
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
C1
|
13
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
E1
|
15
|
Left Join or Left Outer Join:
Left Outer join is used to get the completely data from one table and only matching data from second table
 |
| LEFT OUTER JOIN |
Here is an example of Left Outer Join in LINQ :
var query = from s in _dbContext.Students
join a in _db.StudentAddress on s.StudentID equals a.StudentID into StudentAddressDetails
from address in StudentAddressDetails.DefaultIfEmpty()
select new { s,
address.City };
Lambda Expression :
var query = dbContext.Students.GroupJoin(_db.StudentAddress, s => s.StudentID , a => a.StudentID , (s, a) => new { s, a}).SelectMany(m => m.a.DefaultIfEmpty(),(m,s) => new { m.s, m.a.City});
Output:
Student ID
|
Student Number
|
First Name
|
Last Name
|
Date of Birth
|
City
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Lewis
|
1/23/1985
|
Dublin
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
George
|
4/3/1989
|
Rockville
|
3
|
913
|
Jolly
|
Singh
|
6/7/1986
|
NULL
|
The above query returns the complete list of student record
from students table and its city address, if there is not address record for
any student, it will return student record along with City Default value (NULL).
Cross Join :
Cross join is a Cartesian join and it means Cartesian product of both the tables. This join does not use any condition to join two table and it returns the multiplication of record number of both tables
 |
| CROSS JOIN |
Here is an example of Cross Join in LINQ
var query = from s in _dbContext.Students
a in _db.StudentAddress
select new { s.StudentID ,s.StudentNumber, s.FirstName, a.City, a.Zipcode };
Output:
Student ID
|
Student Number
|
First Name
|
City
|
ZipCode
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Dublin
|
43017
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
Dublin
|
43017
|
3
|
913
|
Jolly
|
Dublin
|
43017
|
1
|
911
|
John
|
Rockville
|
32012
|
2
|
912
|
King
|
Rockville
|
32012
|
3
|
913
|
Jolly
|
Rockville
|
32012
|
The above query returns all records from both tables.
Thanks for visiting!!