Entity Framework is Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) .net framework library, which is
used to update, create or delete record from table. This ORM framework allows
to perform bulk updates of records in efficient manner without making
unnecessary database calls.
In EF, when you want to update any record, first you have to load
record in memory and then you can only update the entity and in bulk update scenario,
it creates extra overload on database server and also degrade performance.
In this post we will covers below points:
·
How does the
entity framework work?
·
How does it
impacts performance in bulk update scenario?
·
How at some level
we can overcome this problem?
What is Entity Framework
?
Entity Framework definition as per MSDN:
“Entity Framework (EF) is an object-relational mapper that enables
.NET developers to work with relational data using domain-specific objects”
Entity Framework works as a layer between database and business
layer (application code) and entity framework maps each database table to
entity class ( C# CLR class) and with help of this entity class, developer can
perform SQL DML operation like create, modify and delete on mapped database
table.
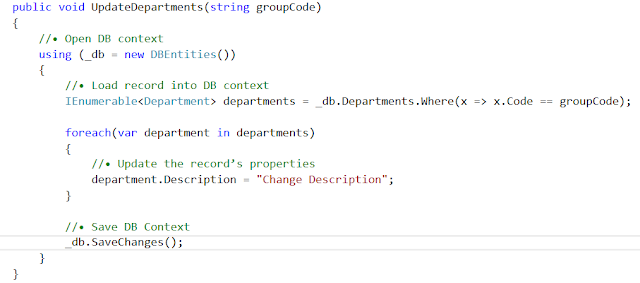
Single Record
Update by using Entity Framework:
Single record update in Entity
framework, is very simple and straight forward
·
Open DB context
·
Load record into
DB context
·
Update the
record’s properties
·
Save DB Context
Bulk Update (Multiple Record
Update) by using Entity Framework:
In bulk record update, we need to pull
records, which are needed to be updated and update each record properties and at
last call SaveChanges() method of DBContext to save all changes.
It
looks pretty and but it will generate SQL update script for each records and
its known problem in Entity framework for bulk operation ( Update or Delete )
and at this time Microsoft does not have any recommended solution instead of
using third party entity framework like EntityFramework.Extended.
Other
Entity framework related Links:




No comments:
Post a Comment